VBET
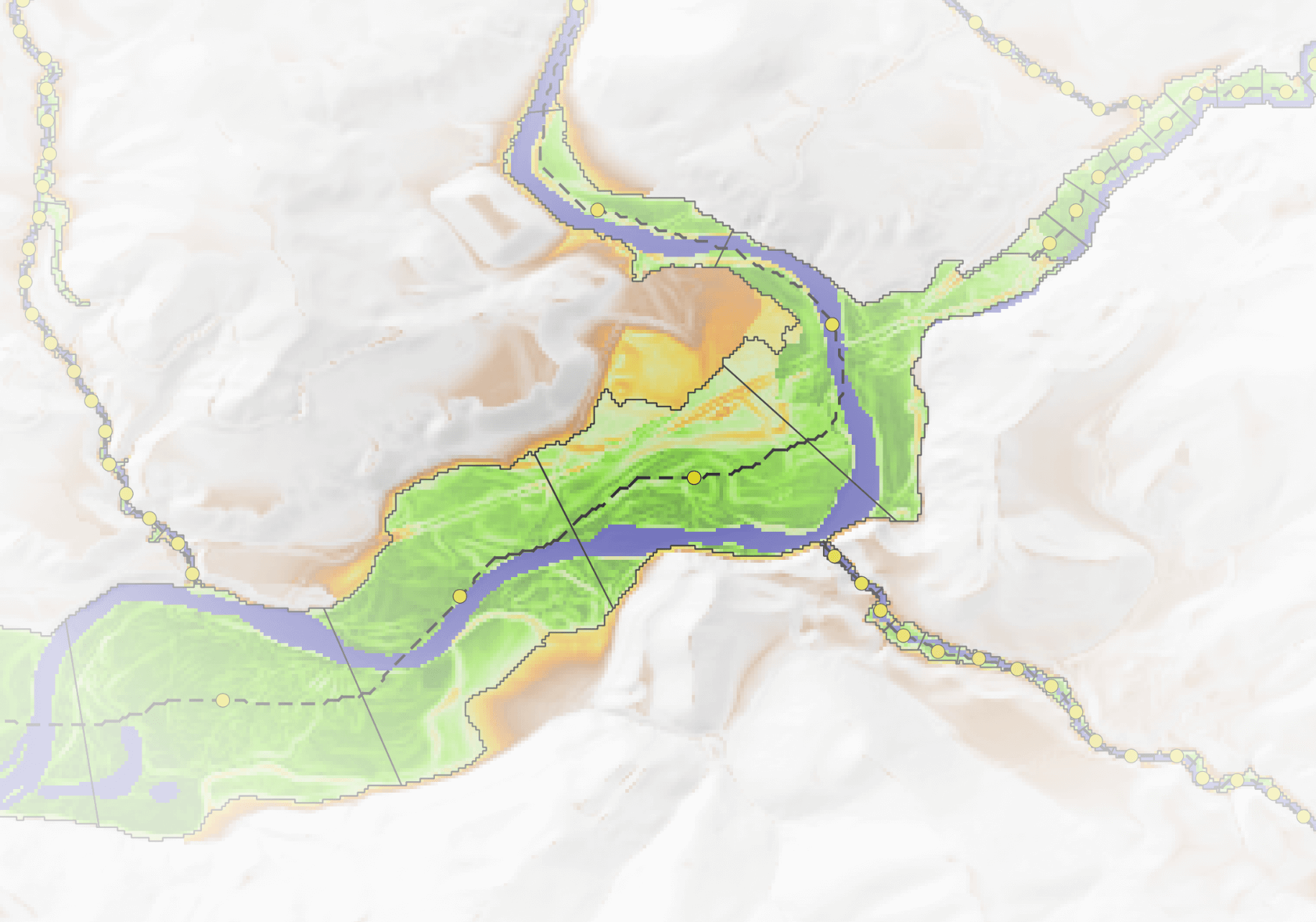
The Valley Bottom Extraction Tool (VBET) identifies and maps the valley bottom of a riverscape, roughly separating it into geomorphic units (channel, low-lying floodplain, and elevated (distal/inactive) floodplain).
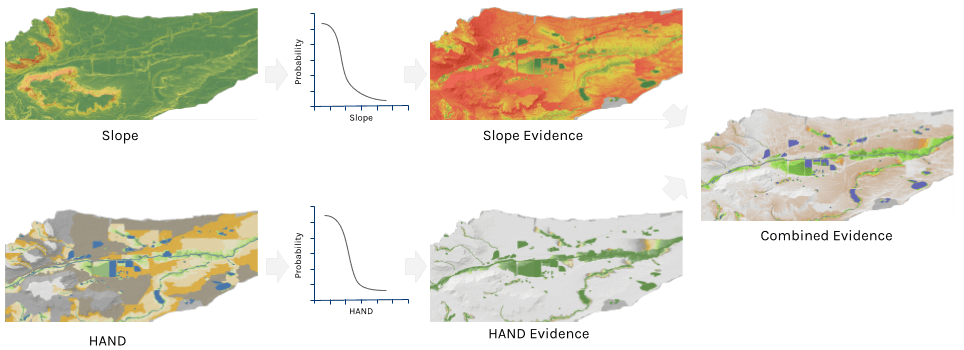
VBET uses a digital elevation model (DEM) and a channel area polygon as inputs. VBET determines valley bottom with combined lines of evidence from two topographic analyses of the DEM (slope raster and Height Above Nearest Drainage (HAND) raster) and a channel area polygon rasterized. These can be generated by the TauDEM and Channel Area tools respectively.
VBET interprets lines of evidence by converting input rasters into values between 0 (very low likelihood of being valley bottom) and 1 (very high likelihood). These values are calibrated with transform functions based on stream size, recognizing that smaller streams typically have higher slopes than larger river settings. Similarly, higher values of HAND (higher elevations above the drainage network) are less likely to be part of the valley bottom in smaller streams. VBET averages these transformed inputs using different weights, resulting in a raster with values between 0 and 1, representing relative probability of being part of the valley bottom.
For a detailed description of the algorithm, see the Algorithm page.
Additionally, VBET segments the valley bottom output into Discrete Geographic Objects (DGOs), polygons that vary in size depending on river scale. Each DGO serves as a sample unit for analyzing riverscape characteristics, and VBET automatically calculates a suite of metrics for each one.
At the center of each DGO, VBET places an Integrated Geographic Object (IGO)—a point used to summarize metrics over a moving window of adjacent DGOs.
Both DGOs and IGOs include a range of calculated metrics. For a detailed description of the metrics, see the Metrics page.
Resources
Download VBET Projects
Discover VBET model run projects available in the Riverscapes Data Exchange.
Latest Version Change Log
Release notes tracking changes, bug fixes and issues.

Source Code
VBET is open source under the GNU general public license. The code is available on GitHub.
References
- Gilbert J.T., Macfarlane W.W. & Wheaton J.M., 2016. The Valley Bottom Extraction Tool (V-BET): A GIS tool for delineating valley bottoms across entire drainage networks. Computers and Geosciences. DOI: 10.1016/j.cageo.2016.07.014.